Can we treat autoimmune disease with 'inverse' vaccines?
Scientists hope a new type of vaccine could help treat autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis (MS), Type 1 diabetes, allergic asthma, or Crohn's disease.
In autoimmune diseases, the body's immune system — our defense against illness — can't tell the difference between good cells and bad cells, and ends up attacking them all. So you get sick either way.
But in a study published in Nature Biomedical Engineering this month, the scientists say a so-called "inverse vaccine" helped them stop an immune response from attacking healthy cells when it was faced with a laboratory model of an autoimmune disease.
Jeffrey Hubbell, who led the research, told DW that inverse vaccines were "a whole new concept of vaccination" that may one day treat many autoimmune diseases.
The vaccine is still in development, and has not been tested on humans.
What is an inverse vaccine?
Conventional vaccines train the immune system to spot infectious diseases and stop them from multiplying and spreading.
Take the COVID-19 vaccine, for example. It contains elements that represent the coronavirus spike protein — the thing that attaches itself to cells and infects them, and makes you sick.
If you've had a COVID vaccine, your body should be able to recognize that spikey shape of the virus attached to a cell and kill it.
An inverse vaccine, on the other hand, stops the immune system from attacking cells — specifically, good, healthy cells.
Instead, it retrains the immune system to save healthy cells, essentially by adding a "do not attack" flag.
What illnesses might inverse vaccines treat?
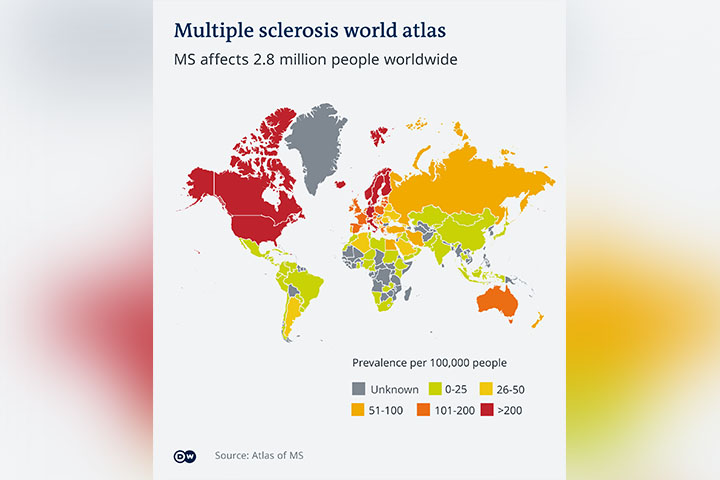
Researchers hope inverse vaccines will be used to treat a variety of auto-immune diseases, including MS, where immune cells attack cells of the brain and spinal cord, or in Type I diabetes, where immune cells attack the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
Autoimmune diseases are usually treated with drugs that suppress the immune system to stop the immune cells from attacking any cells, including healthy ones. They can be effective, but have their disadvantages, too.
"By dampening down the immune [system], patients can't fight infectious disease as well [as they would otherwise], and don't response well to vaccines, [so] they're more susceptible to diseases [in general]," said Hubbell.
The inverse vaccine works differently. Instead of giving a general message to the immune system to dampen it down, it gives a specific message to stop attacking the body's own — healthy — cells.
"[It] suppresses a dysfunctional immune response, leaving the healthy parts of the immune system intact," said Chris Jewell, a bioengineer at University of Maryland, US, who also works on inverse vaccines but was not involved in the study.
How adaptable are inverse vaccines to different diseases?
The concept of an inverse vaccine is not new. It was pioneered by Stanford researcher Lawrence Steinman in the early 2000s.
But Hubbell says his research offers a new approach to creating adjustable inverse vaccines, specific to different autoimmune diseases.
"The basic structure [of the vaccine] can be applied to different diseases. We're also working on food allergies and allergic asthma," said Hubbell.
When will inverse vaccines be ready for patients?
Hubbell's inverse vaccine is not yet ready for testing in human trials, and no other inverse vaccines have been clinically approved, either.
But early safety trials are under way, including for their use with celiac disease, an autoimmune disease associated with eating wheat, barley and rye, and Phase 1 safety trials for MS.
"A lot of the first indications of success are [with] celiac disease, so you could treat people to respond better to gluten. It could be really transformative," said Jewell.
Jewell said they hoped to see more developments in the field of inverse vaccines in the next five to ten years.
01 Oct 2023,08:56













 Live Tv
Live Tv